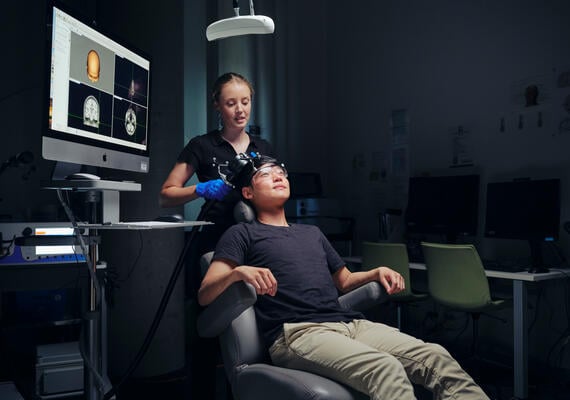
Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS)
TMS stimulates the brain by delivering brief, magnetic pulses from a coil held against the scalp. It’s used to study the relationship between brain activity, cognition and behaviour.
Our cognitive neuroscience facilities located at our Burwood Campus are purpose-built for researchers and psychology students to examine the relationship between brain structure, cognition and behaviour. You’ll have access to equipment that allows you to investigate the human mind using the latest cognitive neuroscience techniques.
tDCS stimulates the brain by delivering weak electrical currents from electrodes against the scalp. It’s used to examine task performance via the relationship between brain activity, cognition and behaviour.
Neuronavigation uses a brain scan to determine targets for TMS application, increasing the accuracy by allowing us to see exactly where we are applying TMS. Used in clinical groups to personalise TMS treatment.
EEG measures brain activity via small electrodes on the scalp. It helps us understand the link between brain activity and cognitive processes, like memory and perception.
Examine, analyse and visualise participant data and run MRI analyses using technical software packages.

TMS stimulates the brain by delivering brief, magnetic pulses from a coil held against the scalp. It’s used to study the relationship between brain activity, cognition and behaviour.
Get the hands-on experience and industry connections you need to build a diverse and rewarding career in the psychology and mental health sector.
We have an amazing, diverse range of researchers and fields of research, so I knew the Cognitive Neuroscience Unit was the right place for me to do my PhD. You feel like you’re not just a student, but more like you’re doing an internship and you’re learning from your colleagues.
Pamela Barhoun
Electromyography (EMG) measures a muscle’s electrical activity through small electrodes that are placed on the skin. EMG is often used in combination with TMS, to stimulate the brain’s motor cortex and record responses in hand muscles.
Near infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) measures blood volume in the brain to provide measure of brain activity. NIRS can be used to investigate frontal lobe activity while a person is performing a verbal creativity task.
Eye tracking uses an infrared camera to determine where, and for how long, a person is looking at an item. It's a strong indicator of visual attention and can be combined with other neuroscience techniques to better uncover the relationship between brain, cognition and behaviour.
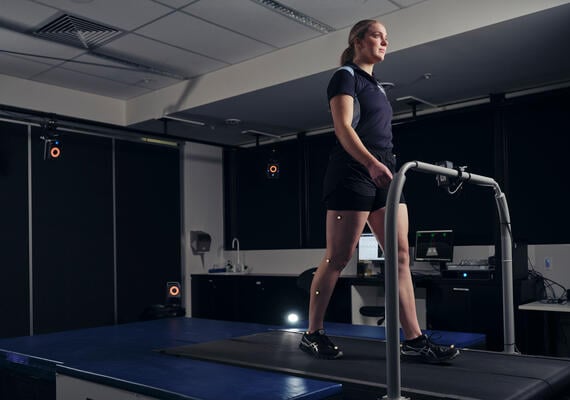

A gait analysis walkway measures the subtle aspects of a person’s walk, considering their balance, step length and step timing, through thousands of tiny sensors that are embedded in a mat where the person walks. It can be used as an investigative tool in diagnosis.
We have a strong research culture and a proud history of applying findings to clinical practice, education programs and policy. Our school is home to the Cognitive Research Unit where we translate research into action.
If you have further questions about our cognitive neuroscience facilities, please get in touch.