Hardness testing
Hardness is not a fundamental property of a material, but rather defined as 'the resistance the material exhibits to permanent deformation by penetration of another harder material'. The principal purpose of the hardness test is to determine the suitability of a material, or the particular treatment to which the material has been subjected. The quantitative value of hardness should always be evaluated in relation to:
- the type of indenter and its geometry
- the given load on the indenter
- a specific loading time profile and a specific load duration.
Methods
Instrument factors can be categorised by applied load, indentation, indenter and others. The below table shows the different parameters of each factor that can affect hardness testing.
Factors that influence hardness testing
Conversion tables
There are many conversion tables that exist. Many are material dependent. Care must be taken when using conversion tables to ensure hardness values are being reported accurately.

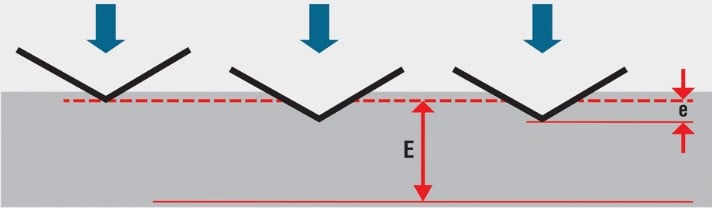 Calculated by measuring the depth of an indent, after an indenter has been forced into the specimen material at a given load.
Calculated by measuring the depth of an indent, after an indenter has been forced into the specimen material at a given load.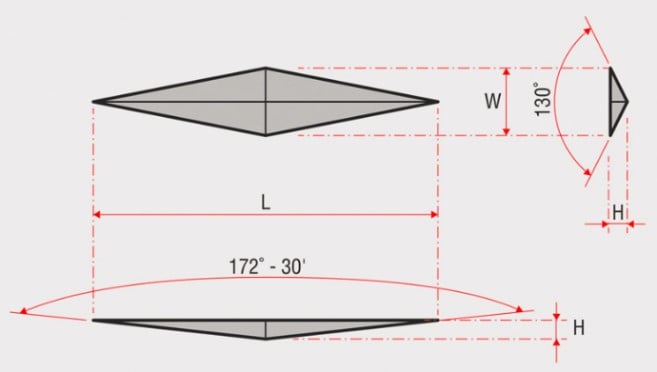 Calculated by measuring the size of the long diagonal of an indent left by introducing an asymmetrical pyramidal diamond with a given load into the sample material.
Calculated by measuring the size of the long diagonal of an indent left by introducing an asymmetrical pyramidal diamond with a given load into the sample material.